Environments
Version: 4.3+
Overview
Environments represent different stages in your development lifecycle. They allow you to manage your product releases from local development to production. Projects and feature flags are accessible in all environments, but each environment has different feature flag configurations. This allows you to enable a flag in development or test without enabling it in production.
The default environments are development and production. Unleash instances created before version 4.3 also have an environment called default. Enterprise customers can create, clone, deprecate, and delete environments.
The set of all available environments is defined at the instance level. Additionally, each project can choose which of the environments are visible on the project level. The set of environments available to any given project is always a subset of the environments at the instance level. Each project must always have at least one active environment.
Environment types
Each environment has a name and one of the following types:
- Development
- Test
- Pre-production
- Production
Meeting specific conditions in a given environment type affects a feature's lifecycle stage. For example, a feature that is receiving metrics and is exposed to users in a production environment moves to the live stage. Production environments also display additional confirmation prompts for changes that may impact users. The default production environment is of type production.
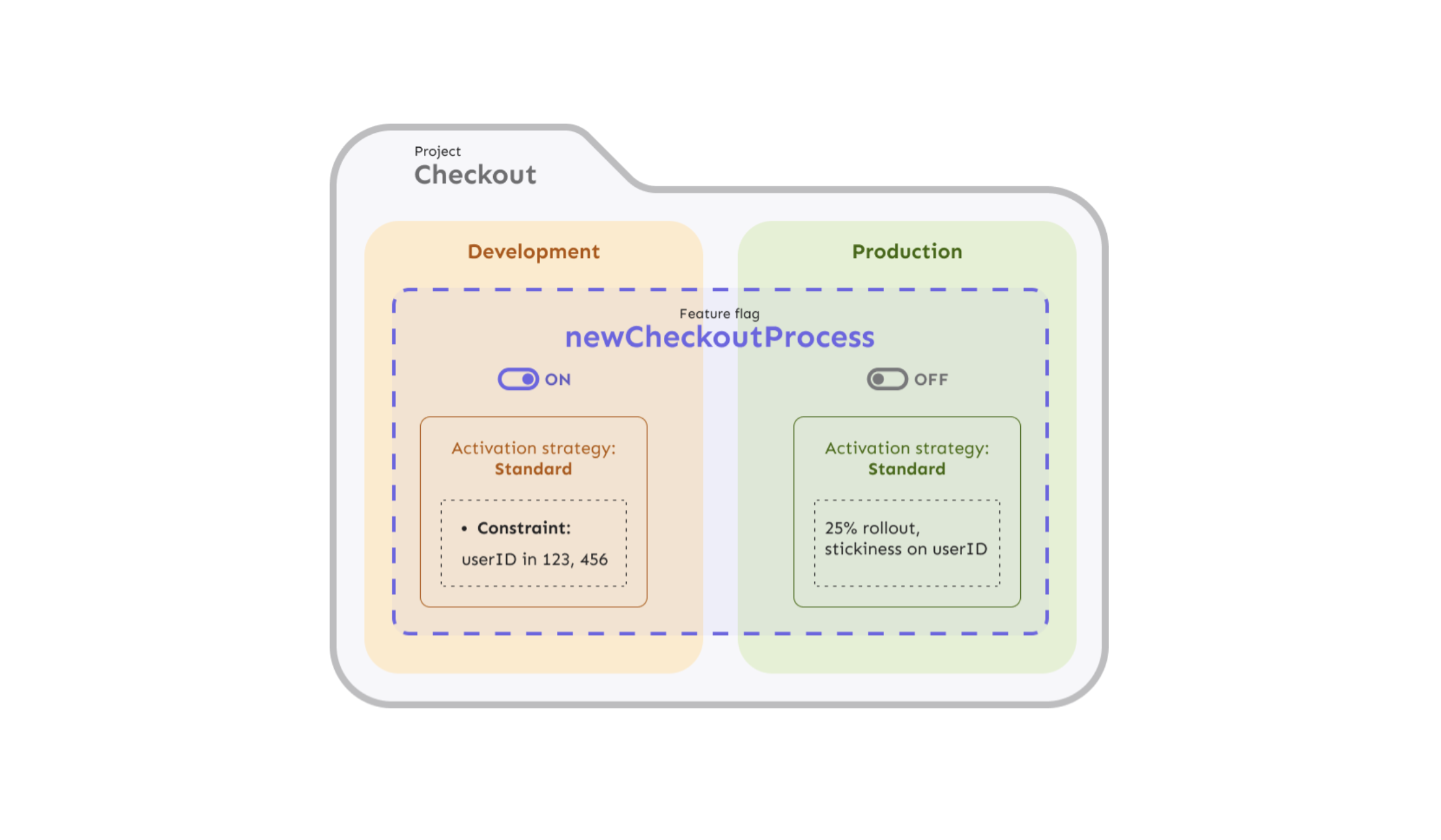
Activation strategies
Activation strategies are the component of feature flags that define who should get a feature. An activation strategy is assigned to one feature flag in one environment. For example, you can use activation strategies to show a feature only to select users in development, but roll it out to 25% of users in production.
Connected applications and usage metrics
When connecting an SDK to Unleash, the API key determines which environment to fetch feature flag configurations for. Therefore, connected applications must use environment-scoped API tokens.
The environment context field in SDKs is a legacy implementation and does not affect environment access.
Unleash tracks usage metrics per environment.
Enable an environment
To enable an environment for a feature flag, you must first add activation strategies for that environment. If you don't define an activation strategy, the default is a gradual rollout to 100% of users.
To enable a feature flag in a specific environment, do the following:
- In the Admin UI, navigate to the feature flag you'd like to enable in an environment.
- In the list of environments, click Add strategy for the environment you want to enable.
- Select your desired strategy type and click Configure.
- Enter a strategy name and define the rollout percentage. Optionally, you can configure segments, constraints, and variants.
- Click Save strategy.
- In the Enabled in environments section, toggle the environment you want to enable.
Clone an environment
Plan: Enterprise | Version: 4.19+
Cloning an environment allows you to duplicate environments, including all feature flag strategies and their states. To clone an environment in the Admin UI, go to Configure > Environments. Under Actions, select Clone for the environment you want to clone.
Cloning an environment creates a copy of the selected source environment. You can select which projects to clone the environment configuration in. This means that the default visibility of the source environment, as well as any feature flag configurations, are cloned in the new environment. For example, if a feature flag had a gradual rollout to 67% in the source environment, then your new environment will have the same feature enabled with the same activation strategy in the new environment. After cloning, the environments are independent and do not stay in sync.
You can also clone the user permissions of the source environment. If you don't clone permissions, only Admins and Editors can make changes in the new environment.